History
During its eight decades as an industry leader, Nippon Yakin Kogyo has brought innovation and technological ingenuity to its products for superior functionality and versatility. From its fire extinguishers in 1925 to stainless steels today that are ideally designed for green technologies, Nippon Yakin Kogyo continues its long tradition of creating excellence.
Okame-no-Men released Nippon Yakin Kogyo's first stainless steel product on October 25, 1935.
Nippon Kako (now Nippon Yakin Kogyo) produced the first stainless steel in 1935 at its Kawasaki Alloy Works.
An okame-no-men, a traditional mask used in the performing arts was purchased from Heiken-ji Temple in Kawasaki and used
as a mold for Nippon Yakin Kogyo’s first product. Based on the mask instead of a typical wooden mold, a sand mold was
created. Stainless steel melted in a 50-kilogram induction furnace was poured into the sand mold, becoming the first
item produced by Nippon Yakin Kogyo.
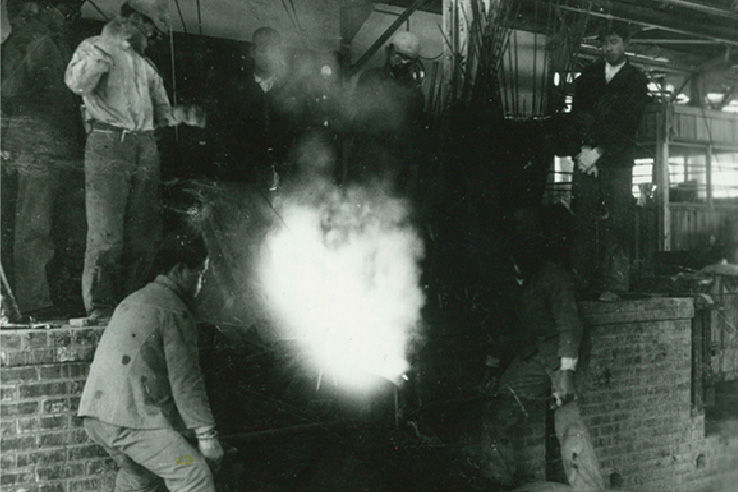 Manufacture of the first stainless steel product
Manufacture of the first stainless steel product
I. Founding Period of Nippon Yakin Kogyo
| 1925 | Chuo Rika Kogyo Co., Ltd. founded as a manufacturer and seller of fire extinguishers |
|---|---|
| 1928 | Renamed Nippon Kako Co., Ltd. and became a manufacturer of fireworks, government-commissioned manufacturer and seller of blasting supplies, and seller of explosives |
| 1934 |
Constructed Kawasaki Field Office (Daishigawara , Kawasaki City) Established Oheyama Nickel Mining Industry Co., Ltd. (predecessor of Oheyama Nickel Kogyo Co., Ltd.) Started Construction of the Kawasaki Alloy Works (later the Kawasaki Works) and entered metal refining industry. |
| 1935 | Manufactured the first stainless steel product. |
| 1936 | Started Industrial production of specializedty stainless steel and stainless steel |
| 1939 | Introduced company emblem (logo of two wheels) |
| 1942 |
Stock listed on the Tokyo and Osaka stock exchanges Renamed Nippon Yakin Kogyo Co., Ltd. |
| 1943 |
Merged with Oheyama Nickel Kogyo, took over its nickel mining and ferro-nickel smelting business Kawasaki Works renamed Kawasaki Plant Oheyama's Iwataki Smelting Works renamed Iwataki Smelting Plant |
| 1948 | Renamed Iwataki Smelting Plant to Oheyama Plant |
| 1950 | Successfully manufactured stainless steel using the basic oxygen process in an arc furnace*1 at Kawasaki Plant |
| 1956 | Established a research institute at Kawasaki Plant |
| 1957 | Approx. 100,000 tsubo (approx. 330,578 m2) of reclaimed land in Kawasaki acquired from Kanagawa Prefecture |
II. Establishment of a Mass Production System for Stainless Steels
| 1959 | Production of alloy steel and carbon steel discontinued to focus on stainless steel plate |
|---|---|
| 1960 | Started to operate the Sendzimir 20H Cold Strip Mill at Kawasaki Plant NAS*2 trademarked for stainless steel products in Japan |
| 1962 | Started to operate a 30-ton-capacity electric arc furnace*1(the first large furnace operated by a stainless steel manufacturer in Japan) |
| 1965 | Started to operate a continuous casting machine (CCM) at Kawasaki Plant |
| 1966 | Started to operate a planetary mill (for hot rolling) at Kawasaki Plant Received Minister of International Trade and Industry Award for excellent metrological management |
| 1968 | Started to operate a 60-ton-capacity electric arc furnace (furnace No. 8) at Kawasaki Plant |
| 1969 | Received Minister of International Trade and Industry Award for standardization and excellent quality |
| 1970 |
Started to operate a 60-ton-capacity electric arc furnace (furnace No. 9) at Kawasaki Plant Started to operate a continuous casting machine (CCM No. 2, 5-foot width) at Kawasaki Plant Received Minister of Labour Award for excellence in vocational training |
| 1971 |
Started to operate a cold-rolling mill (20H Sendzimir Mill No. 3) at Kawasaki Plant Started to operate the 60-ton-capacity VOD*3 process at Kawasaki Plant |
| 1975 | Spun off Oheyama Plant, transferred to Oheyama Nickel Co. |
| 1977 | Started to operate the AOD*4 process at Kawasaki Plant |
| 1983 | Merged with Oheyama Nickel Co., and renamed Oheyama Plant |
| 1989 |
Head office relocated to present location of Sanei Bldg. (1-chome Kyobashi, Chuo-ku, Tokyo) Completed the expansion of the second cold strip mill shop (5AP*5, HKline *6, and finishing equipment) at Kawasaki Plant (world's first combined CAP*7 (5AP*5)) |
| 1990 |
Started to operate CTS*8 at Kawasaki Plant Started to operate No. 5 rotary kiln at Oheyama Plant Kawasaki Plant commended by the Governor of Kanagawa Prefecture as an excellent high-pressure gas worksite |
| 1991 | Established central logistics center inside Kawasaki Plant |
| 1993 | Kawasaki Plant received TPM Excellence Award |
| 1994 |
Oheyama Plant received TPM Excellence Award Kawasaki Plant received ISO 9002 certification |
III. Capital Investment to Be More Competitive and Sales Promotion for High-Performance Alloys
| 1996 | Started to operate a new hot-rolling mill at Kawasaki Plant |
|---|---|
| 1999 |
Kawasaki Plant received ISO 14001 certification Oheyama Plant received ISO 14001 certification |
| 2002 | Received John Chipman Award (the Iron & Steel Society (now the Association for Iron & Steel Technology)), as a first specialized stainless steel manufacturer |
| 2003 |
Opened Shanghai representative office Spun off Kawasaki Plant and Oheyama Plant (Established Yakin Kawasaki and Yakin Oheyama) |
| 2008 | Started to operate a new AOD at Yakin Kawasaki |
| 2009 | Yakin Kawasaki obtained Occupational Safety and Health Management System (OSHMS) certification |
| 2010 | Merged Yakin Kawasaki and Yakin Oheyama |
| 2011 | Established Nippon Yakin America Inc(subsidiary in USA) |
| 2012 |
Established Nippon Yakin Shanghai Co., Ltd. (subsidiary in China) Established Nippon Yakin Europe Ltd. (subsidiary in UK) |
| 2014 | Established Nippon Yakin Asia Pte. Ltd. (subsidiary in Singapore) |
| 2015 | Obtained NORSOK (Norwegian petroleum standard) certification |
| 2018 | Founded Chinese joint venture, NISCO Nippon Yakin Kogyo Nanjing Co., Ltd. |
| 2022 | Started to operate a new electric furnace ("E furnace") |
| 2024 | Started to operate a new Cold Strip Mill("No.4 HZR") |
| 2025 | Established Nippon Yakin India Private Limited(subsidiary in Mumbai) |
*1 Arc furnace:Electric furnace for melting metals
*2 NAS steel:Name of Nippon Yakin Kogyo's standard and brand name given to products in Japan, created from the first letters of
*4 AOD:Argon oxygen decarburization
*5 5AP:Abbreviation for Nippon Yakin Kogyo's 5th annealing and pickling line
*6 HK line:Product polishing line (our original name)
*7 Combined CAP:Continuous annealing and pickling line for cold rolled strips that is combined with a skin-pass rolling mill and levelling equipment
*8 CTS:Original name given to Nippon Yakin Kogyo's equipment used to adjust composition and temperature of molten steel in the finishing process
*2 NAS steel:Name of Nippon Yakin Kogyo's standard and brand name given to products in Japan, created from the first letters of
NIPPON-YAKIN
AUSTENITE(main structural organization of stainless steel)
STAINLESS STEEL
*4 AOD:Argon oxygen decarburization
*5 5AP:Abbreviation for Nippon Yakin Kogyo's 5th annealing and pickling line
*6 HK line:Product polishing line (our original name)
*7 Combined CAP:Continuous annealing and pickling line for cold rolled strips that is combined with a skin-pass rolling mill and levelling equipment
*8 CTS:Original name given to Nippon Yakin Kogyo's equipment used to adjust composition and temperature of molten steel in the finishing process